What Is The Leading Controllable Risk Factor For All Forms Of Cardiovascular Disease?
What you lot'll learn to practise: draw concrete changes in late adulthood

In this section, you'll larn more about concrete changes in tardily adulthood. While late machismo is mostly a time of concrete decline, there are no set rules as to when and how it happens. We are continually learning more almost how to promote greater health during the aging procedure.
Watch It
Lookout man this clip from Marco Pahor, a professor in the University of Florida department of aging and geriatric research, equally he discusses his research about ways physical activeness affects the mobility of older adults and how it may upshot in longer life, lower medical costs, and increased long-term independence.
Learning outcomes
- Describe age categories of late adulthood
- Explicate trends in life expectancies, including factors that contribute to longer life
- Depict chief aging, including vision and hearing loss
- Explicate secondary aging concerns that are mutual in late adulthood, including illnesses and diseases
- Describe and compare theories of aging
Defining Late Adulthood
Defining Late Adulthood: Age or Quality of Life?

Effigy 1. 82-year old body architect Ernestine Shepard is quoted with saying, "Yous're not getting quondam; you're getting ready."
We are considered in late adulthood from the fourth dimension we reach our mid-sixties until death. Because nosotros are living longer, tardily adulthood is getting longer. Whether nosotros start counting at 65, as demographers may suggest, or later, there is a greater proportion of people alive in late adulthood than anytime in world history. A 10-year-old child today has a 50 per centum chance of living to age 104. Some demographers take fifty-fifty speculated that the first person always to alive to be 150 is alive today.
Virtually 15.2 percent of the U.South. population or 49.2 million Americans are 65 and older.[i] This number is expected to grow to 98.2 million by the yr 2060, at which time peoplein this historic period group will comprise virtually 1 in four U.Due south. residents. Of this number, xix.seven million volition be age 85 or older. Developmental changes vary considerably amongst this population, then it is farther divided into categories of 65 plus, 85 plus, and centenarians for comparison by the census.[ii]
Demographers use chronological age categories to classify individuals in tardily adulthood. Developmentalists, still, dissever this population in to categories based on concrete and psychosocial well-being, in order to describe i'south functional age. The "young old" are healthy and active. The "old old" experience some health issues and difficulty with daily living activities. The "oldest sometime" are delicate and often in demand of care. A 98 year onetime adult female who still lives independently, has no major illnesses, and is able to take a daily walk would exist considered as having a functional age of "immature former". Therefore, o ptimal crumblingrefers to those who enjoy amend wellness and social well-being than average.
Normal aging refers to those who seem to accept the same health and social concerns every bit nearly of those in the population. Nonetheless, there is withal much being done to empathise exactly what normal aging ways. Impaired aging refers to those who experience poor health and dependence to a greater extent than would be considered normal. Aging successfully involves making adjustments as needed in order to continue living equally independently and actively as possible. This is referred to as selective optimization with compensation. Selective Optimization With Bounty is a strategy for improving health and well being in older adults and a model for successful aging. Information technology is recommended that seniors select and optimize their all-time abilities and most intact functions while compensating for declines and losses. This ways, for instance, that a person who tin can no longer drive, is able to observe alternative transportation, or a person who is compensating for having less energy, learns how to reorganize the daily routine to avoid over-exertion. Perhaps nurses and other allied health professionals working with this population will begin to focus more on helping patients remain independent by optimizing their best functions and abilities rather than on simply treating illnesses. Promoting health and independence are essential for successful aging.
Sentry It: Aging Successfully
Systematic test of one-time age is a new field inspired by the unprecedented number of people living long enough to go elderly. Developmental psychologists Paul and Margret Baltes take proposed a model of adaptive competence for the entire life bridge, simply the emphasis hither is on old age. Their model SOC (Pick, Optimization, and Compensation) is illustrated with engaging vignettes of people leading fulfilling lives, including writers Betty Friedan and Joan Erikson, and dancer Bud Mercer. Segments of the cognitive tests used past the Baltes in assessing the mental abilities of older people are shown. Although the video clip show beneath is old and dated, information technology remains an intellectually appealing video in which the Baltes discuss personality components that mostly lead to positive crumbling experiences.
Endeavor Information technology
Age Categories
Senescence, orbiologicalaging, is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics.[3]

Figure 2.The word senescence, tin exist traced back to Latin senex, meaning "old." Lots of other English words come from senex—senile, senior, senate, etc. The word senate to describe a legislative assembly dates back to aboriginal Rome, where the Senatus was originally a council of elders composed of the heads of patrician families. There's also the much rarer senectitude, which, like senescence, refers to the state of beingness sometime (specifically, to the final stage of the normal life span).
The Young Old—65 to 74
These 18.3 one thousand thousand Americans tend to written report greater health and social well-existence than older adults. Having good or excellent health is reported by 41 per centum of this age group (Center for Disease Command, 2004). Their lives are more similar to those of midlife adults than those who are 85 and older. This group is less likely to crave long-term care, to be dependent or to be poor, and more likely to be married, working for pleasance rather than income, and living independently. About 65 percent of men and 50 percent of women between the ages of 65-69 continue to work total-time (He et al., 2005).
Concrete activeness tends to decrease with age, despite the dramatic wellness benefits enjoyed by those who exercise. People with more education and income are more probable to continue being physically active. And males are more likely to appoint in concrete action than are females. The majority of the young-old continue to alive independently. Only well-nigh 3 percent of those 65-74 need help with daily living skills every bit compared with about 22.nine percent of people over 85. (Another fashion to consider retrieve of this is that 97 percentage of people betwixt 65-74 and 77 pct of people over 85 do non require assist!) This age group is less likely to experience centre affliction, cancer, or stroke than the quondam, simply most every bit probable to experience depression (U.South. Census, 2005).
The One-time Old—75 to 84
This historic period group is more likely to feel limitations on physical activity due to chronic illness such as arthritis, center atmospheric condition, hypertension (peculiarly for women), and hearing or visual impairments. Rates of expiry due to heart disease, cancer, and cognitive vascular disease are double that experienced past people 65-74. Poverty rates are 3 percent higher (12 percent) than for those between 65 and 74. Nevertheless, the majority of these 12.9 meg Americans live independently or with relatives. Widowhood is more than common in this group-especially among women.
The Oldest Old—85 plus
The number of people 85 and older is 34 times greater than in 1900 and now includes 5.seven 1000000 Americans. This grouping is more likely to crave long-term care and to be in nursing homes. However, of the 38.9 one thousand thousand American over 65, just 1.vi million crave nursing home care. Sixty-eight percent live with relatives and 27 percentage live alone (He et al., 2005; U. S. Census Bureau, 2011).
Figure iii. Kirk Douglas, player and filmmaker, is a centenarian.
The Centenarians
Centenarians, or people aged 100 or older, are both rare and distinct from the rest of the older population. Although uncommon, the number of people living past age 100 is on the rise; between the year 2000 and 2014, and then number of centarians increased past over 43.vi%, from 50,281 in 2000 to 72,197 in 2014.[four] In 2010, over half (62.5 percent) of the 53,364 centenarians were age 100 or 101.[5]
This number is expected to increment to 601,000 by the year 2050 (U. South. Census Bureau, 2011). The majority is between ages 100 and 104 and eighty percent are women. Out of near seven billion people on the planet, about 25 are over 110. Near live in Japan, a few live the in United States and three alive in France (National Institutes of Health, 2006). These "super-Centenarians" have led varied lives and probably do not requite us whatsoever unmarried answers virtually living longer. Jeanne Clement smoked until she was 117. She lived to be 122. She too ate a nutrition rich in olive oil and rode a bike until she was 100. Her family unit had a history of longevity. Pitskhelauri (in Berger, 2005) suggests that moderate diet, continued work and activity, inclusion in family and customs life, and exercise and relaxation are important ingredients for long life.
Blue Zones
Recent research on longevity reveals that people in some regions of the world alive significantly longer than people elsewhere. Efforts to study the mutual factors between these areas and the people who live there is known as blue zone research. Blue zones are regions of the world where Dan Buettner claims people alive much longer than boilerplate. The term first appeared in his November 2005 National Geographic magazine cover story, "The Secrets of a Long Life." Buettner identified 5 regions equally "Blue Zones": Okinawa (Nippon); Sardinia (Italy); Nicoya (Republic of costa rica); Icaria (Greece); and the Seventh-day Adventists in Hill Linda, California. He offers an explanation, based on data and first mitt observations, for why these populations live healthier and longer lives than others.
The people inhabiting bluish zones share common lifestyle characteristics that contribute to their longevity. The Venn diagram beneath highlights the following six shared characteristics among the people of Okinawa, Sardinia, and Loma Linda blue zones. Though non a lifestyle choice, they also live equally isolated populations with a related gene pool.
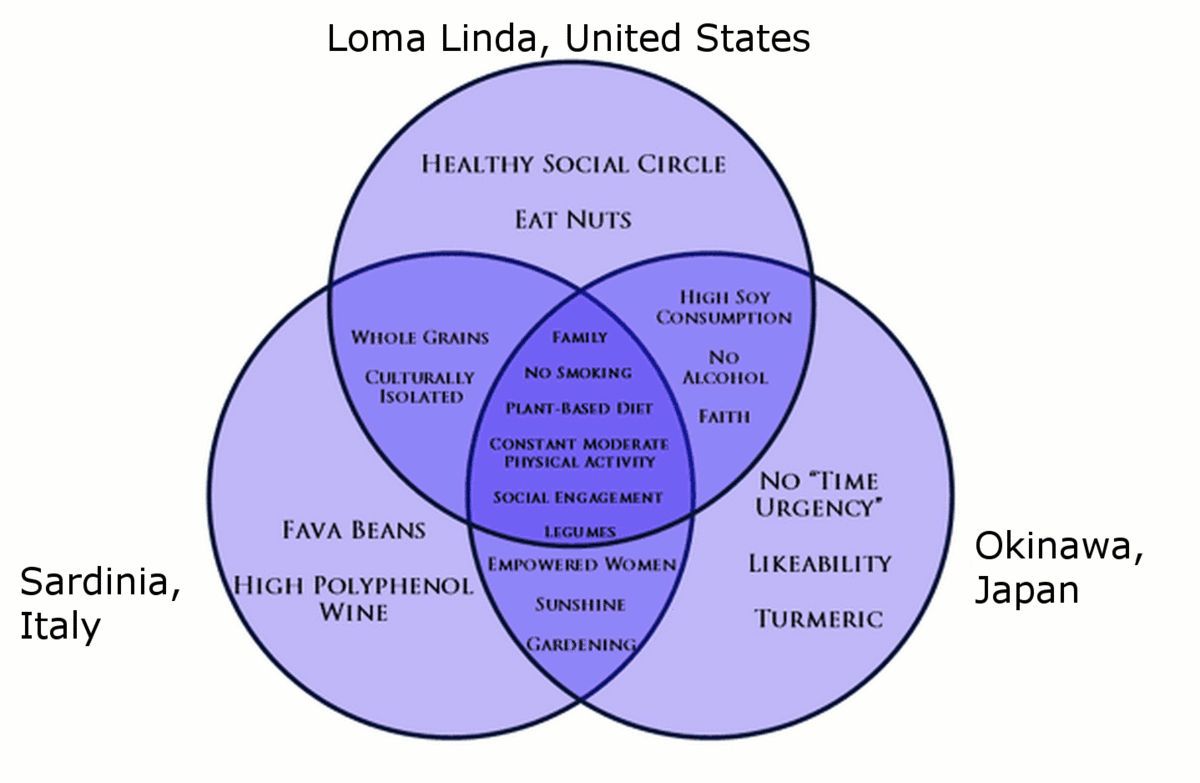
Figure 4. Blue zones share many mutual healthy habits contributing to longer lifespans.
- Family unit – put ahead of other concerns
- Less smoking
- Semi-vegetarianism – the bulk of food consumed is derived from plants
- Abiding moderate physical activeness – an inseparable part of life
- Social engagement – people of all ages are socially agile and integrated into their communities
- Legumes – commonly consumed
In his volume, Buettner provides a listing of nine lessons, covering the lifestyle of blue zones people:
- Moderate, regular physical activeness.
- Life purpose.
- Stress reduction.
- Moderate caloric intake.
- Plant-based diet.
- Moderate alcohol intake, specially wine.
- Engagement in spirituality or faith.
- Date in family unit life.
- Engagement in social life.
Try Information technology
The "Graying" Population and Life Expectancy
The "Graying" of America
The term "graying of America" refers to the fact that the American population is steadily becoming more dominated by older people. In other words, the median historic period of Americans is going upwards.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau's 2017 National Population Projections, the twelvemonth 2030 marks an important demographic turning signal in U.S. history. Past 2030, all baby boomers will be older than age 65. This volition expand the size of the older population and then that one in every 5 residents will be retirement age. And by 2035, information technology's projected that in that location will be 76.7 million people under the age of 18 but 78 meg people above the age of 65. [6]

Figure 5. 2030 marks an of import demographic change as international migration is expected to overtake natural increase in the United States.
The 2030s are projected to exist a transformative decade for the U.S. population. The population is expected to grow at a slower pace, age considerably and become more racially and ethnically diverse. Cyberspace international migration is projected to overtake natural increase in 2030 equally the primary driver of population growth in the United States, another demographic showtime for the Usa.
Although births are projected to be nearly four times larger than the level of cyberspace international migration in coming decades, a rising number of deaths volition increasingly offset how much births are able to contribute to population growth. Between 2020 and 2050, the number of deaths is projected to rise substantially as the population ages and a significant share of the population, the baby boomers, age into older adulthood. As a outcome, the population volition naturally grow very slowly, leaving net international migration to overtake natural increase as the leading cause of population growth, even as projected levels of migration remain relatively constant.[7]
"Graying" Around the World
While the world's oldest countries are mostly in Europe today, some Asian and Latin American countries are quickly catching up. The percentage of the population anile 65 and over in 2015 ranged from a high of 26.6 percentage for Nihon to a depression of around 1 percentage for Qatar and United Arab Emirates. Of the world'south 25 oldest countries, 22 are in Europe, with Germany and Italia leading the ranks of European countries for many years (He, Goodkind, and Kowal, 2015).
By 2050, Slovenia and Bulgaria are projected to be the oldest European countries. Nippon, yet, is currently the oldest nation in the world and is projected to retain this position through at least 2050. With the rapid aging taking identify in Asia, the countries of South korea, Hong Kong, and Taiwan are projected to join Japan at the peak of the listing of oldest countries and areas by 2050, when more than than one-third of these Asian countries' total populations are projected to exist anile 65 and over.[8]
Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the twelvemonth of birth, current historic period and other demographic factors including gender. The most unremarkably used measure of life expectancy is at birth (LEB). There are corking variations in life expectancy in different parts of the world, mostly due to differences in public wellness, medical care, and nutrition, but also afflicted by education, economic circumstances, violence, mental health, and sex.

Figure 6. Life expectancies around the world in 2015.
Life Expectancy in the United States
According to the CDC (Centers for Disease Command and Prevention), life expectancy in the U.South. now stands at 78.7 years. Women proceed to outlast men, with life expectancy being 76.iii years for males, and 81.one years for females. Life expectancy varies co-ordinate to race and ethnicity. It is highest for Hispanics, for both males and females, and lower for blacks than for whites or Hispanics.

Effigy 7. Life expectancy at birth, by race and Hispanic origin: United States, 2013 and 2014. From CDC/NCHS, National Vital Statistics Organisation, Mortality.
Statistics from the U.Due south. Census Bureau reveal that the 85-and over age group is the fastest-growing historic period group in America. Co-ordinate to the Census Bureau and AgingStats.gov, the over-65 population grew from 3 million in 1900 to 40 million in 2010, an increase of more than 1200%. But during this same time, the over-85 population grew from but over 100,000 in 1900 to five.v one thousand thousand in 2010–an increase of 5400%!
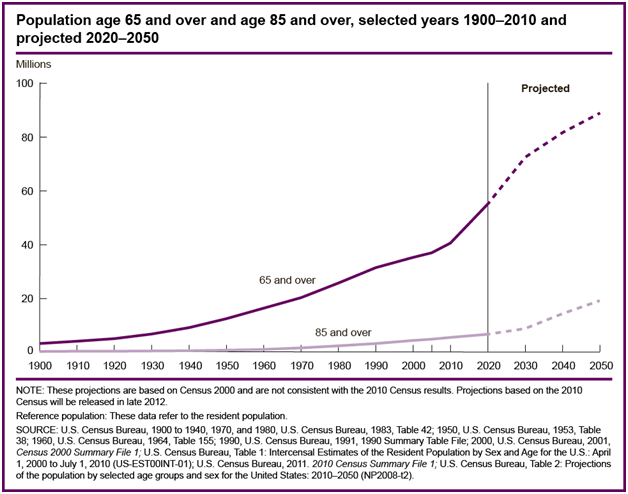
Effigy 8. The elderly population is projected to grow significantly in the coming decades. Retrieved from https://partners4prosperity.com//wp-content/uploads/2014/09/aging-85-and-over.gif.
When calculating life expectancy, nosotros consider all of the elements of heredity, health history, current wellness habits, and electric current life experiences which contribute to a longer life or subtract from a person's life expectancy. Recent studies concluded that cut calorie intake by 15 percent over two years can slow crumbling and protect against diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer's.[9]
Some life factors are beyond a person'southward control, and some are controllable. The rising price of wellness care is a source of financial vulnerability to older adults. Vaccines are especially of import for older adults. As you get older yous're more than probable to get diseases like the influenza, pneumonia, and shingles, and to accept complications that can pb to long-term disease, hospitalization, and even death.
Things that contribute to longer life expectancies include eating a healthy diet that is rich in plants and basics. Staying physically active, not smoking, and consuming moderate amounts of alcohol, tea, or coffee are also reported to be beneficial to leading a long life. Other recommendations include being conscientious, prioritizing your happiness, avoiding stress and anxiety, and having a strong social support network. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and maintaining between vii-8 hours of sleep per night is also benign.[10]
A major reason a person will statistically live longer once they reach an older historic period is merely that they accept made it this far without annihilation killing them. Also, there appears to exist several factors which may explain changes in life expectancy in the United States and around the world—health conditions are amend, m whatever diseases have been eliminated or better controlled through medicine, working conditions are better and b etter lifestyles choices are existence made. Such factors significantly contribute to longer life expectancies.
Life Expectancy Tables
Sometimes referred to mortality tables, death charts or actuarial life tables, these life expectancy tables are strictly statistical, and practise non accept into consideration any personal health information or lifestyle information. Have a look at life expectancy tables on the Life Expectancy Calculators website.
Endeavor It
Understanding Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is also used in describing the physical quality of life.Quality of lifeis the general well-beingness of individuals and societies, outlining negative and positive features of life. Quality of life considers life satisfaction, including everything from physical health, family, didactics, employment, wealth, safe, security, freedom, religious beliefs, and the environment.

Figure ix. Physical action remains low for those above historic period 65, although practice tin can have tremendous health benefits and effect in longer life expectancy.
Increased life expectancy brings business organization over the wellness and independence of those living longer. Greater attention is now being given to the number of years a person can expect to live without disability, which is called active life expectancy. When this distinction is made, we encounter that although women live longer than men, they are more at risk of living with inability (Weitz, 2007).
What factors contribute to poor health in women? Union has been linked to longevity, simply spending years in a stressful spousal relationship can increase the risk of affliction. This negative issue is experienced more by women than men and seems to accumulate through the years. The impact of a stressful marriage on wellness may not occur until a woman reaches 70 or older (Umberson, Williams, et. al., 2006). Sexism can too create chronic stress. The stress experienced by women every bit they work outside the dwelling equally well every bit treat family members tin can also ultimately have a negative impact on wellness (He et als, 2005).
The shorter life expectancy for men in general, is attributed to greater stress, poorer attention to health, more interest in dangerous occupations, and higher rates of death due to accidents, homicide, and suicide. Social support can increment longevity. For men, life expectancy and health seems to amend with marriage. Spouses are less probable to appoint in risky health practices and wives are more probable to monitor their hubby'southward diet and health regimes. Simply men who live in stressful marriages can also feel poorer health every bit a event.
Health and Sexuality
It has been suggested that an active sex activity life can inc rease longevity among the elderly.[11] Dr. Maggie Syme constitute in her enquiry on sexuality in erstwhile historic period that, "Having a sexual partnership, with frequent sexual expression, having a good quality sex life, and being interested in sexual activity have been institute to exist positively associated with health among centre-aged and older adults."[12] Positive sexual health in older age is gradually becoming more of a mutual topic and less taboo. Population pct increment amid older Americans has resulted in placing more attention on the needs of this age grouping, including their ideas on sexual health, desires, and attitudes. This shift in attitudes and behaviors, combined with medical advances to prolong a sexually active life, has inverse the landscape of aging sexuality.
In that location are a number of associated health benefits with practicing positive sexual wellness. Positive sexual health frequently acts equally a de-stressor promoting increased relaxation. Researchers also report wellness benefits such as decreased pain sensitivity, improved cardiovascular health, lower levels of low, increased self-esteem, and ameliorate relationship satisfaction.This could likewise imply that in that location are negative consequences of poor sexual wellness or lack of sexual activity, including depression, low cocky-esteem, increased frustration, and loneliness.
Primal players in improving the quality of life amidst older adults are the adults themselves. By exercising, reducing stress, not smoking, limiting use of alcohol, consuming more than fruits and vegetables, and eating less meat and dairy, older adults can await to alive longer and more active lives (He et. als, 2005).Regular exercise is also associated with a lower gamble of developing neurodegenerative disorders, especially Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's affliction. Stress reduction both in late machismo and earlier in life is too crucial. The reduction of societal stressors can promote agile life expectancy. In the final 40 years, smoking rates have decreased, but obesity has increased, and physical activity has only modestly increased.
Try It
Wellness in Belatedly Machismo: Main Aging
Normal Aging
The Baltimore Longitudinal Study on Aging (BLSA, 2011) began in 1958 and has traced the aging process in 1,400 people from age twenty to 90. Researchers from the BLSA have institute that the aging process varies significantly from private to individual and from one organ system to some other. Kidney part may deteriorate earlier in some individuals. Bone strength declines more than rapidly in others. Much of this is determined by genetics, lifestyle, and disease. However, some generalizations about the aging procedure have been found:
- Heart muscles thicken with age
- Arteries become less flexible
- Lung capacity diminishes
- Brain cells lose some functioning but new neurons can also be produced
- Kidneys become less efficient in removing waste product from the claret
- The float loses its ability to shop urine
- Body fat stabilizes and then declines
- Musculus mass is lost without practice
- Bone mineral is lost. Weight bearing exercise slows this down.
Link to Learning
Watch this video clip from the National Constitute of Wellness equally it explains the enquiry involved in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study on Crumbling. Y'all'll see some of the tests done on individuals, including measurements on energy expenditure, force, proprioception, and brain imaging and scans. Watch the The Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA) here.

Effigy 10. Principal crumbling includes inevitable changes such equally skin that becomes more than wrinkled and less rubberband.
Chief and Secondary Aging
Healthcare providers demand to be aware of which aspects of crumbling are reversible and which ones are inevitable. By keeping this distinction in heed, caregivers may be more objective and accurate when diagnosing and treating older patients. And a positive attitude can go a long way toward motivating patients to stick with a health authorities. Unfortunately, stereotypes can lead to misdiagnosis. For example, it is estimated that about x percentage of older patients diagnosed with dementia are actually depressed or suffering from another psychological illness (Berger, 2005). The failure to recognize and care for psychological problems in older patients may be i consequence of such stereotypes.
Primary Aging
Senescence is the biological aging is the gradual deterioration offunctional characteristics. Information technology is the process by which cells irreversibly finish dividing and enter a state of permanent growth arrest without undergoing cell death. This process is also referred to asprimary crumbling and thus, refers to the inevitable changes associated with crumbling (Busse, 1969). These changes include changes in the skin and hair, height and weight, hearing loss, and centre disease. However, some of these changes tin can exist reduced past limiting exposure to the sun, eating a nutritious diet, and exercising.
Skin and hair alter with age. The skin becomes drier, thinner, and less rubberband during the aging process. Scars and imperfections get more noticeable equally fewer cells grow underneath the surface of the skin. Exposure to the sun, or photoaging, accelerates these changes. Graying hair is inevitable, and hair loss all over the body becomes more prevalent.
Height and weight vary with age. Older people are more than than an inch shorter than they were during early on adulthood (Masoro in Berger, 2005). This is thought to be due to a settling of the vertebrae and a lack of muscle strength in the back. Older people weigh less than they did in mid-life. Bones lose density and tin become brittle. This is especially prevalent in women. However, weight training tin help increase os density after but a few weeks of training.
Muscle loss occurs in late adulthood and is most noticeable in men as they lose musculus mass. Maintaining strong leg and heart muscles is of import for independence. Weight-lifting, walking, swimming, or engaging in other cardiovascular and weight begetting exercises tin can help strengthen the muscles and prevent atrophy.
Vision
Some typical vision issues that arise along with aging include:
- Lens becomes less transparent and the pupils shrink.
- The optic nerve becomes less efficient.
- Afar objects get less acute.
- Loss of peripheral vision (the size of the visual field decreases by approximately one to three degrees per decade of life.)[13]
- More light is needed to run into and it takes longer to adjust to a change from low-cal to darkness and vice versa.
- Driving at night becomes more challenging.
- Reading becomes more of a strain and eye strain occurs more than easily.
The bulk of people over 65 have some difficulty with vision, just almost is hands corrected with prescriptive lenses. Three percent of those 65 to 74 and eight percent of those 75 and older take hearing or vision limitations that hinder action. The nearly common causes of vision loss or damage are glaucoma, cataracts, age-related macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy (He et al., 2005).
- Glaucoma occurs when force per unit area in the fluid of the eye increases, either considering the fluid cannot drain properly or because too much fluid is produced. Glaucoma can be corrected with drugs or surgery. It must be detected early enough.
- Cataracts arecloudy or opaque areas of the lens of the eye that interfere with passing light, oft develop.Cataracts can be surgically removed or intraocular lens implants can replace old lenses.
- Macular degeneration is the about mutual cause of incomprehension in people over the historic period of 60. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) affects the macula, a yellowish area of the centre located near the retina at which visual perception is well-nigh acute.A diet rich in antioxidant vitamins (C, E, and A) tin can reduce the risk of this disease.
- Diabetic retinopathy, likewise known as diabetic eye disease, is a medical condition in which damage occurs to theretina due todiabetes mellitus. It is a leading cause ofblindness. There are three major treatments for diabetic retinopathy, which are very effective in reducing vision loss from this affliction: laser photocoagulation, grand edications, surgery.
Hearing
Hearing Loss, is experienced by 25% of people between ages 65 and 74, then past 50% of people above age 75.[fourteen] Amidst those who are in nursing homes, rates are even higher. Older adults are more likely to seek aid with vision damage than with hearing loss, perhaps due to the stereotype that older people who have difficulty hearing are also less mentally alert.
Conductive hearing loss may occur because of historic period, genetic predisposition, or environmental furnishings, including persistent exposure to extreme racket over the course of our lifetime, certain illnesses, or damage due to toxins. Conductive hearing loss involves structural harm to the ear such equally failure in the vibration of the eardrum and/or movement of the ossicles (the three basic in our center ear). Given the mechanical nature by which the sound wave stimulus is transmitted from the eardrum through the ossicles to the oval window of the cochlea, some degree of hearing loss is inevitable. These problems are often dealt with through devices like hearing aids that amplify incoming sound waves to make vibration of the eardrum and movement of the ossicles more than likely to occur.
When the hearing trouble is associated with a failure to transmit neural signals from the cochlea to the brain, it is called sensorineural hearing loss. This blazon of loss accelerates with historic period and tin can be caused by prolonged exposure to loud noises, which causes harm to the hair cells within the cochlea. Presbycusis is age-related sensorineural hearing loss resulting from degeneration of the cochlea or associated structures of the inner ear or auditory nerves. The hearing loss is most marked at higher frequencies. Presbycusis is the second most mutual disease adjacent to arthritis in aged people.
One disease that results in sensorineural hearing loss is Ménière's disease. Although not well understood, Ménière's disease results in a degeneration of inner ear structures that tin lead to hearing loss, tinnitus (constant ringing or buzzing), vertigo (a sense of spinning), and an increase in force per unit area within the inner ear (Semaan & Megerian, 2011). This kind of loss cannot be treated with hearing aids, simply some individuals might be candidates for a cochlear implant as a handling option. Cochlear implants are electronic devices consisting of a microphone, a speech processor, and an electrode array. The device receives incoming sound information and directly stimulates the auditory nerve to transmit data to the brain.
Existence unable to hear causes people to withdraw from conversation and others to ignore them or shout. Unfortunately, shouting is normally high pitched and can be harder to hear than lower tones. The speaker may also begin to utilise a patronizing course of 'infant talk' known aselderspeak (Meet et al., 1999). This language reflects the stereotypes of older adults every bit existence dependent, demented, and childlike. Hearing loss is more prevalent in men than women. And information technology is experienced by more white, non-Hispanics than by Black men and women. Smoking, centre ear infections, and exposure to loud noises increase hearing loss.
Nutrition and Crumbling Research
The Jean Mayer Human Diet Research Center on Aging (HNRCA), located in Boston, Massachusetts, is one of six human nutrition enquiry centers in the United States supported past the United States Department of Agriculture and Agricultural Enquiry Service. The goal of the HNRCA, which is managed past Tufts University, is to explore the human relationship between nutrition, physical activeness, and salubrious and active aging.
The HNRCA has made meaning contributions to U.S. and international nutritional and physical activity recommendations, public policy, and clinical healthcare. These contributions include advancements in the knowledge of the role of dietary calcium and vitamin D in promoting diet and bone health,the role of nutrients in maintaining the optimal immune response, the prevention of infectious diseases, the role of nutrition in prevention of cancer, obesity inquiry,modifications to the Food Guide Pyramid,contribution to USDA food information bank, advancements in the study of sarcopenia, heart disease,vision, encephalon and cognitive function,front of packaging nutrient labeling initiatives,and research of how genetic factors bear on predisposition to weight gain and various health indicators. Enquiry clusters within the HNRCA address four specific strategic areas: i) cancer, 2) cardiovascular affliction, three) inflammation, immunity, and infectious illness and 4) obesity.
WAtch IT
Enquiry done past T. Colin Campbell M.D., Michael Greger One thousand.D., Neal Bernard G.D. and others take demonstrated the bear on of diet upon longevity and quality of life. As discussed in the video below, consumption of less animal based poly peptide has been linked with the slowing of degradation of function which was traditionally seen every bit part of the normal aging process.
Main crumbling can be compensated for through exercise, cosmetic lenses, nutrition, and hearing aids. Just as of import, past reducing stereotypes about aging, people of age tin maintain self-respect, recognize their own strengths, and count on receiving the respect and social inclusion they deserve.
Try It
Health in Late Adulthood: Secondary Aging
Secondary Crumbling
Secondary aging refers to changes that are caused by affliction or affliction. These illnesses reduce independence, impact quality of life, bear upon family members and other caregivers, and bring fiscal burden. The major deviation between primary aging and secondary aging is that primary crumbling is irreversible and is due to genetic predisposition; secondary crumbling is potentially reversible and is a result of affliction, health habits, and other individual differences.
Chronic Illnesses

Figure 11. Secondary crumbling refers to the aspects of crumbling that are non universally shared by anybody, but are brought about by disease or chronic disease.
In the U.s.a., nigh one in two Americans (133 million) has at least one chronic medical condition, with well-nigh subjects (58%) between the ages of 18 and 64. The number is projected to increment by more ane per centum per year by 2030, resulting in an estimated chronically ill population of 171 million. The most common chronic conditions are high blood pressure level, arthritis, respiratory diseases similar emphysema, and high cholesterol.
According to inquiry by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, chronic illness is also especially a business organisation in the elderly population in America. Chronic diseases like stroke, heart affliction, and cancer are amid the leading causes of expiry amid Americans anile 65 or older. While the majority of chronic conditions are found in individuals between the ages of 18 and 64, it is estimated that at to the lowest degree 80% of older Americans are currently living with some form of a chronic condition, with 50% of this population having two or more chronic conditions. The two most common chronic conditions in the elderly are high blood force per unit area and arthritis, with diabetes, coronary heart disease, and cancer also being reported at loftier rates amid the elderly population. The presence of type ii diabetes, high blood force per unit area, and obesity, is termed "metabolic syndrome" and impacts fifty% of individuals over the age of 60.[15]
Heart illness is the leading crusade of death from chronic disease for adults older than 65, followed by cancer, stroke, diabetes, chronic lower respiratory diseases, influenza and pneumonia, and, finally, Alzheimer'south disease (which nosotros'll examine further when we talk about cognitive refuse). Though the rates of chronic disease differ by race for those living with chronic disease, the statistics for leading causes of death amongst elderly are nearly identical across racial/ethnic groups.
Eye Disease
Equally stated above, eye disease is the leading cause of decease from chronic disease for adults older than 65. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a grade of diseases that involve the heart or claret vessels. CVD includes coronary avenue diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known equally a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, centre failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic eye illness, cardiomyopathy, heart arrhythmia, built heart affliction, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis.
The underlying mechanisms vary depending on the illness. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral avenue disease involve atherosclerosis.This may be caused by high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, and excessive alcohol consumption, amongst others. High blood pressure is estimated to account for approximately thirteen% of CVD deaths, while tobacco accounts for 9%, diabetes 6%, lack of do 6% and obesity 5%.
Information technology is estimated that upwardly to 90% of CVD may be preventable. Prevention of CVD involves improving run a risk factors through: healthy eating, exercise, avoidance of tobacco fume and limiting booze intake. Treating gamble factors, such equally loftier blood pressure, blood lipids and diabetes is as well beneficial. The employ of aspirin in people, who are otherwise healthy, is of unclear benefit.
Cancer
Age in itself is one of the almost important risk factors for developing cancer. Currently, 60% of newly diagnosed malignant tumors and 70% of cancer deaths occur in people anile 65 years or older. Many cancers are linked to aging; these include breast, colorectal, prostate, pancreatic, lung, bladder and tummy cancers. Men over 75 have the highest rates of cancer at 28 per centum. Women 65 and older take rates of 17 percent. Rates for older non-Hispanic Whites are twice as high every bit for Hispanics and non-Hispanic Blacks. The virtually common types of cancer found in men are prostate and lung cancer. Breast and lung cancer are the most common forms in women.
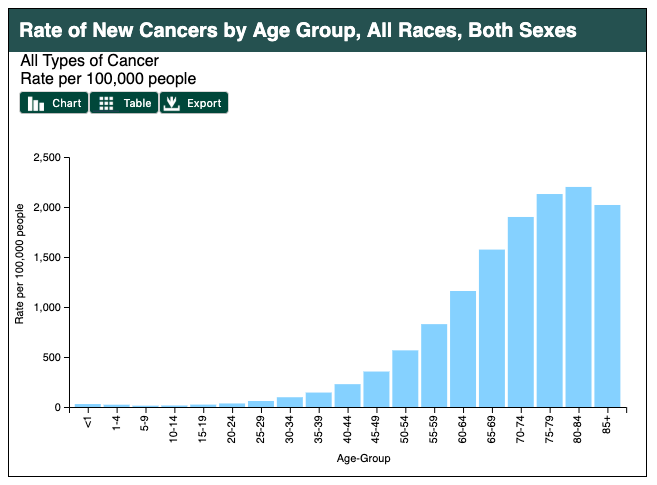
Figure 12. Age is a risk gene for cancer development. Source: https://gis.cdc.gov/Cancer/USCS/DataViz.html.
For many reasons, older adults with cancer have different needs than younger adults with the disease. For instance, older adults:
- May be less able to tolerate sure cancer treatments.
- Have a decreased reserve (the capacity to respond to disease and treatment).
- May take other medical problems in addition to cancer.
- May have functional problems, such as the ability to do basic activities (dressing, bathing, eating) or more than advanced activities (such as using transportation, going shopping or treatment finances), and have less available family support to assistance them as they go through treatment.
- May not always have access to transportation, social support or financial resources.
- May take different views of quality versus quantity of life

Figure xiii. Cancer rates are significantly higher for those above age 65, and is more mutual in men than in women.
Hypertension and Stroke
Hypertension or high blood pressure and associated heart disease and circulatory conditions increase with historic period. Stroke is a leading crusade of decease and severe, long-term disability. Most people who've had a first stroke also had high blood pressure (HBP or hypertension).High claret pressure damages arteries throughout the body, creating conditions where they can burst or clog more easily. Weakened arteries in the brain, resulting from loftier claret pressure, increase the risk for stroke—which is why managing loftier blood pressure is critical to reduce the gamble of having a stroke. Hypertension disables 11.1 percentage of 65 to 74 year olds and 17.1 per centum of people over 75. Rates are higher among women and blacks. Rates are highest for women over 75. Coronary disease and stroke are higher among older men than women. The incidence of stroke is lower than that of coronary illness, but information technology is the No. 5 cause of death and a leading cause of disability in the United states of america.[16] [17]
Arthritis
While arthritis can affect children, it is predominantly a disease of the elderly. Arthritis is more than common in women than men at all ages and affects all races, ethnic groups and cultures. In the United states of america a CDC survey based on data from 2007–2009 showed 22.2% (49.9 million) of adults anile ≥eighteen years had self-reported doc-diagnosed arthritis, and 9.4% (21.1 million or 42.4% of those with arthritis) had arthritis-attributable activity limitation (AAAL). With an crumbling population, this number is expected to increase.
Arthritis is a term often used to mean whatever disorder that affects joints.Symptoms mostly include articulation pain and stiffness.Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In some types of arthritis, other organs are also affected.Onset tin be gradual or sudden.
At that place are over 100 types of arthritis.The nearly common forms are osteoarthritis (degenerative joint illness) and rheumatoid arthritis.Osteoarthritis usually increases in frequency with age and affects the fingers, knees, and hips.Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the easily and feet.Other types include gout, lupus, fibromyalgia, and septic arthritis. They are all types of rheumatic disease
Treatment may include resting the joint and alternating between applying ice and heat. Weight loss and exercise may also be useful. Pain medications such as ibuprofen and paracetamol (acetaminophen) may exist used. In some a articulation replacement may be useful.

Figure fourteen. Articulation pain increases with age.
Older Americans & Cardiovascular Diseases
Visit this statistical fact sheet from the American Heart Clan to larn more about some facts and figures related to heart affliction.
Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known equally adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes characterized by high blood carbohydrate, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. Symptoms may also include increased hunger, feeling tired, and sores that do non heal. Often symptoms come on slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include eye disease, strokes, diabetic retinopathy which tin issue in blindness, kidney failure, and poor claret menstruation in the limbs which may pb to amputations.
Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs equally a result of obesity and lack of exercise. Some people are more genetically at risk than others. Type ii diabetes makes up about ninety% of cases of diabetes, with the other 10% due primarily to type ane diabetes and gestational diabetes. In type 1 diabetes there is a lower total level of insulin to control blood glucose, due to an autoimmune induced loss of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Diagnosis of diabetes is past blood tests such as fasting plasma glucose, oral glucose tolerance test, or glycated hemoglobin (A1C).
Type two diabetes is partly preventable by staying a normal weight, exercising regularly, and eating properly. Treatment involves practice and dietary changes. If claret carbohydrate levels are non adequately lowered, the medication metformin is typically recommended. Many people may eventually also crave insulin injections. In those on insulin, routinely checking blood carbohydrate levels is advised; however, this may not be needed in those taking pills. Bariatric surgery often improves diabetes in those who are obese.
Rates of type ii diabetes take increased markedly since 1960 in parallel with obesity. As of 2015 at that place were approximately 392 meg people diagnosed with the affliction compared to around 30 million in 1985. Typically information technology begins in middle or older historic period, although rates of type 2 diabetes are increasing in young people. Type two diabetes is associated with a x-year-shorter life expectancy.

Figure xv. In 1990, 2.52% of the total population had diabetes. It'due south now ix% of total, 12% of adults. It'southward estimated that 25% of adults will have diabetes in the US by 2030, 33% by 2050.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis comes from the Greek give-and-take for "porous bones" and is a disease in which bone weakening increases the risk of a cleaved bone. It is defined every bit having a bone density of two.5 standard deviations below that of a healthy young adult. Osteoporosis increases with age as basic become brittle and lose minerals. It is the most common reason for a cleaved bone amidst the elderly.
Osteoporosis becomes more than common with age. About fifteen% of white people in their 50s and 70% of those over 80 are affected. Information technology is four times more likely to bear on women than men—in the developed earth, depending on the method of diagnosis, 2% to 8% of males and ix% to 38% of females are affected. In the United states in 2010, about eight million women and ane to 2 million men had osteoporosis. White and Asian people are at greater risk are more likely to have osteoporosis than non-Hispanic blacks.
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous organisation which mainly affects the motor organization, although every bit the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms go increasingly common. Early in the illness, the nearly obvious symptoms are shaking, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking, but thinking and behavioral problems may also occur. Dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the affliction, and depression and anxiety also occur in more than a 3rd of people with PD.
The crusade of Parkinson's illness is mostly unknown, but believed to involve both genetic and ecology factors. Those with a family fellow member affected are more than likely to get the disease themselves. There is also an increased hazard in people exposed to certain pesticides and amid those who have had prior head injuries, while there is a reduced risk in tobacco smokers (though smokers are at a substantially greater chance of stroke) and those who drink coffee or tea. The motor symptoms of the disease event from the expiry of cells in the substantia nigra, a region of the midbrain, which results in non enough dopamine in these areas. The reason for this jail cell decease is poorly understood, but involves the build-up of proteins into Lewy bodies in the neurons.
In 2015, PD affected 6.ii million people and resulted in about 117,400 deaths globally. Parkinson's disease typically occurs in people over the age of 60, of which nigh one pct are affected. Males are more frequently afflicted than females at a ratio of around 3:2. The average life expectancy post-obit diagnosis is betwixt seven and 14 years. People with Parkinson's who have increased the public'southward awareness of the condition include actor Michael J. Pull a fast one on, Olympic cyclist Davis Phinney, and professional boxer Muhammad Ali.
Endeavor Information technology
Theories on Aging

Effigy 16. In that location are several plausible theories as to why crumbling happens
Why do we age?
At that place are a number of attempts to explain why nosotros age and many factors that contribute to aging. The peripheral slowing hypothesis suggests that overall processing speed declines in the peripheral nervous system, affecting the brain's ability to communicate with muscles and organs. Some of the peripheral nervous organisation (PNS) is nether a person's voluntary command, such as the nerves carrying instructions from the brain to the limbs. Too equally decision-making muscles and joints, the PNS sends all the information from the senses back to the brain.
The generalized slowing hypothesis theory suggests that processing in all parts of the nervous system, including the brain, are less efficient with age. This may be why older people have more accidents. Genetics, nutrition, lifestyle, activity, and exposure to pollutants all play a role in the aging process.[eighteen] [19] [20]
Prison cell Life
Cells separate a limited number of times and and then stop. This miracle, known every bit theHayflick limit, is evidenced in cells studied in test tubes which divide near 50 times before condign senescent. In 1961, Dr. Hayflick theorized that the man cell's ability to divide is express to approximately 50-times, after which they simply cease dividing (the Hayflick limit theory of aging). According to telomere theory, telomeres have experimentally been shown to shorten with each successive cell division.[21]
Senescent cells do not die. They simply stop replicating. Senescent cells tin help limit the growth of other cells which may reduce take chances of developing tumors when younger, just tin can alter genes afterward in life and result in promoting the growth of tumors every bit we age (Dollemore, 2006). Express cell growth is attributed to telomeres which are the tips of the protective blanket effectually chromosomes. Each time cells replicate, the telomere is shortened. Eventually, loss of telomere length is thought to create damage to chromosomes and produce prison cell senescence.
Link to Learning
Lookout man this Ted talk past molecular biologist Elizabeth Blackburn on "The Science of Cells That Never Get Old." Blackburn won a Nobel Prize for her pioneering work on telomeres and telomerase, which may play primal roles in how we age.
Biochemistry and Aging
Free Radical Theory of Crumbling
Thefree radical theory of crumbling (FRTA) states that organisms historic period because cells accumulate costless radical damage over time. A free radical is whatever atom or moleculewhich has a single unpaired electron in an outer beat out. This ways that as oxygen is metabolized, mitochondria in the cells catechumen the oxygen to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which provides energy to the cell. Unpaired electrons are a byproduct of this process and these unstable electrons cause cellular damage as they notice other electrons with which to bail. These gratis radicals have some benefits and are used past the immune system to destroy bacteria. However, cellular impairment accumulates and eventually reduces functioning of organs and systems. Many food products and vitamin supplements are promoted as age-reducing. Antioxidant drugs have been shown to increase the longevity in nematodes (pocket-sized worms), but the power to irksome the crumbling process past introducing antioxidants in the diet is still controversial.

Figure 17. In chemistry, a free radical is any atom, molecule, or ion with an unpaired valence electron
Protein Crosslinking
This theory focuses on the role claret sugar, or glucose, plays in the crumbling of cells. Glucose molecules attach themselves to proteins and form chains or crosslinks. These crosslinks reduce the flexibility of tissue and thus it becomes stiff and loses operation. The circulatory system becomes less efficient as the tissue of the heart, arteries and lungs lose flexibility. Joints grow potent equally glucose combines with collegen.
Dna Harm
Through the normal growth and crumbling procedure, DNA is damaged by environmental factors such as toxic agents, pollutants, and lord's day exposure (Dollemore, 2006). This results in deletions of genetic fabric, and mutations in the DNA duplicated in new cells. The accumulation of these errors results in reduced functioning in cells and tissues. Theories that suggest that the body'southward DNA genetic lawmaking contains a built-in fourth dimension limit for the reproduction of human cells are called the genetic programming theories of aging. These theories promote the view that the cells of the body can merely duplicate a certain number of times and that the genetic instructions for running the body tin can be read but a sure number of times earlier they become illegible. Such theories also promote the existence of a "death gene" which is programmed to direct the body to deteriorate and die, and the idea that a long life after the reproductive years is unnecessary for the survival of the species.[22]
Refuse in the Immune System
Equally we age, B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes become less agile. These cells are crucial to the immune arrangement equally they secrete antibodies and directly attack infected cells. The thymus, where T-cells are manufactured, shrinks as aging progresses. This reduces our body'southward ability to fight infection (Berger, 2005).
Attempt It
Glossary
- agile life expectancy:
- the number of years a person can expect to live without inability
- arthritis:
- arthritis is inflammation of one or more of the joints, characterized by articulation pain and stiffness, which typically worsen with age
- blueish zones:
- regions of the globe where Dan Buettner claims people live much longer than average
- centenarians:
- people aged 100 or older
- cochlear implant:
- electronic device that consists of a microphone, a voice communication processor, and an electrode assortment to directly stimulate the auditory nerve to transmit information to the brain
- conductive hearing loss:
- failure in the vibration of the eardrum and/or motion of the ossicles
- free radical theory of aging (FRTA):
- theory that organisms age because cells accumulate free radical damage over time
- generalized slowing hypothesis:
- the theory that processing in all parts of the nervous organization, including the brain, is less efficient
- Hayflick limit:
- the number of times a normal homo jail cell population volition divide earlier jail cell partitioning stops
- hypertension:
- high blood pressure that tin lead to severe complications and increases the chance of middle affliction, stroke, and death
- life expectancy:
- a statistical measure out of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the yr of its nascence, its electric current historic period and other demographic factors including gender
- Ménière'south disease:
- results in a degeneration of inner ear structures that tin can lead to hearing loss, tinnitus, vertigo, and an increase in pressure within the inner ear
- osteoporosis:
- a condition in which the bones become brittle, fragile, and thin, often brought about by a lack of calcium in the nutrition
- Parkinson's disease:
- long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system which mainly affects the motor system, outset characterized past shaking, rigidity, slowness of move, and difficulty with walking, but thinking and behavioral problems may besides occur
- peripheral slowing hypothesis:
- the theory that overall processing speed declines with age in the peripheral nervous organization
- presbycusis:
- age-related sensorineural hearing loss resulting from degeneration of the cochlea or associated structures of the inner ear or auditory fretfulness
- primary crumbling:
- crumbling that is irreversible and is due to genetic predisposition
- secondary aging:
- refers to changes that are caused by illness or disease
- Selective Optimization with Compensation (SOC):
- a strategy for improving health and well being in older adults and a model for successful aging
- senescence:
- biological aging and the gradual deterioration of functional abilities
- sensorineural hearing loss:
- failure to transmit neural signals from the cochlea to the encephalon
- quality of life:
- the full general well-being of individuals and societies, including life satisfaction, concrete wellness, family, didactics, employment, wealth, safety, security, freedom, religious beliefs, and the environment
- temporal theory of pitch perception:
- sound'southward frequency is coded by the activity level of a sensory neuron
- type 2 diabetes (T2D):
- diabetes characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin primarily from obesity or lack of exercise
- vertigo:
- spinning awareness
What Is The Leading Controllable Risk Factor For All Forms Of Cardiovascular Disease?,
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wmopen-lifespandevelopment/chapter/physical-development-in-late-adulthood/
Posted by: wymersuchaticke51.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is The Leading Controllable Risk Factor For All Forms Of Cardiovascular Disease?"
Post a Comment